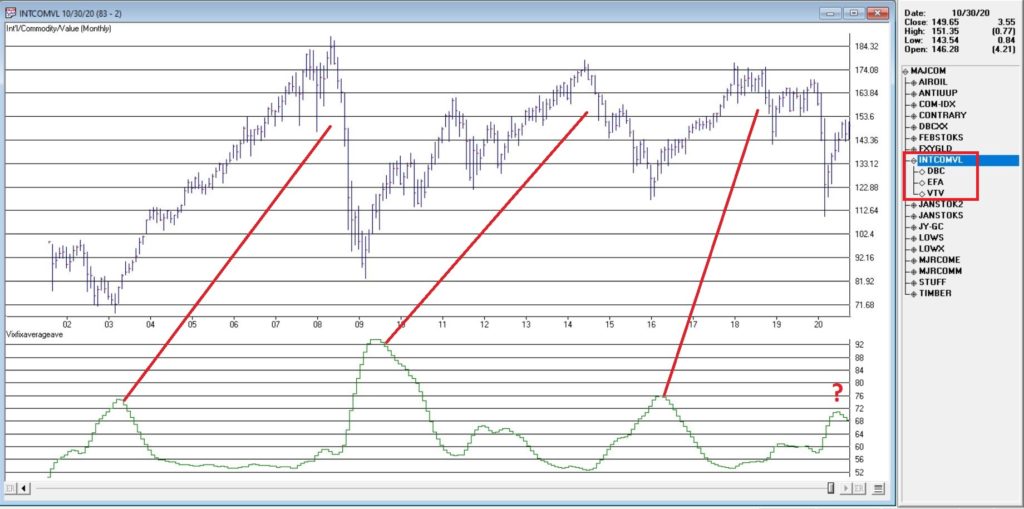
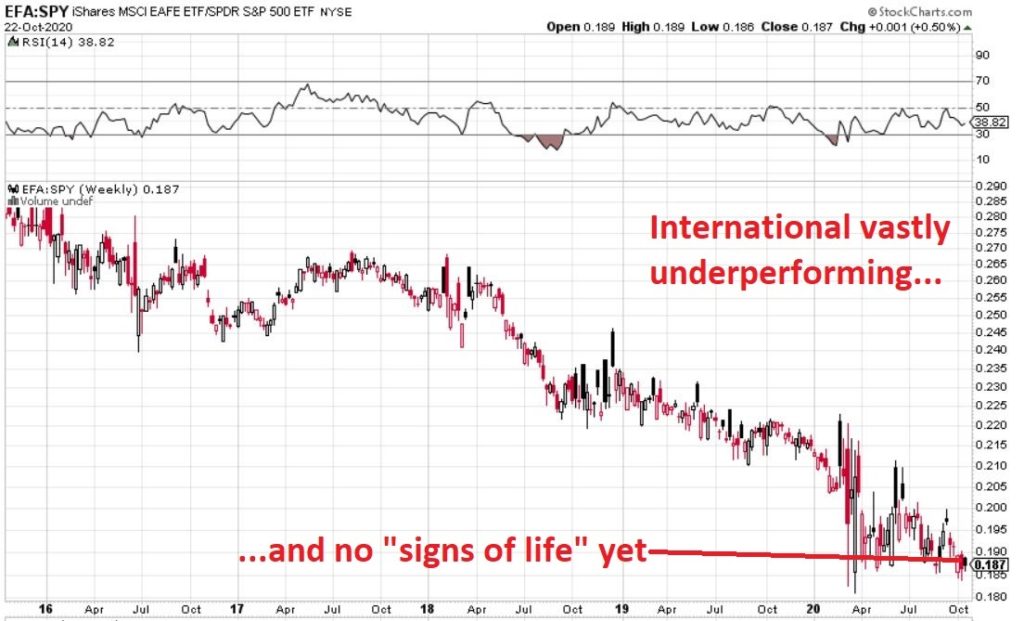
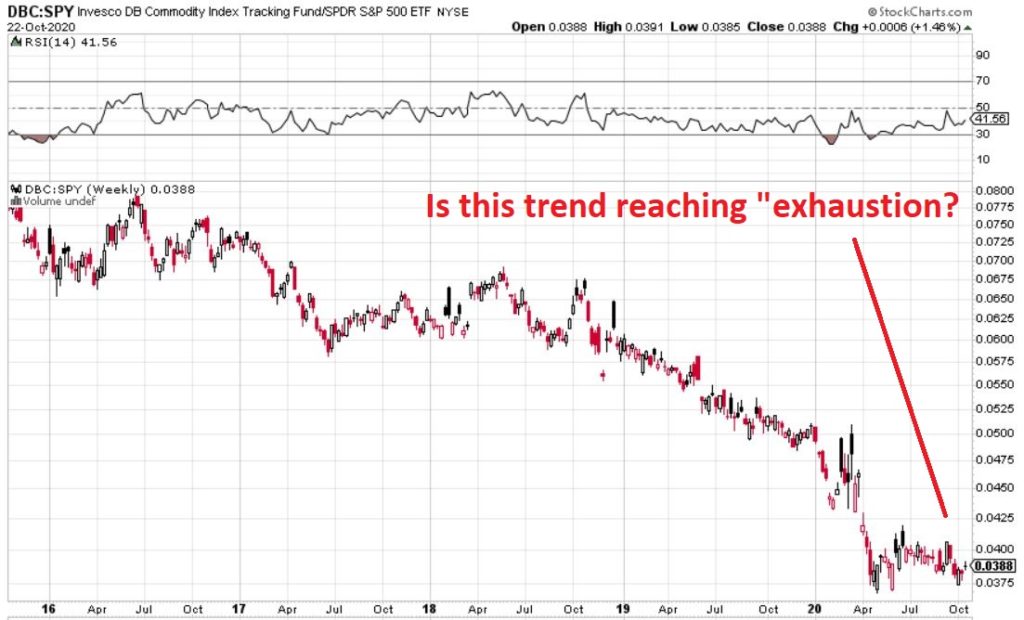
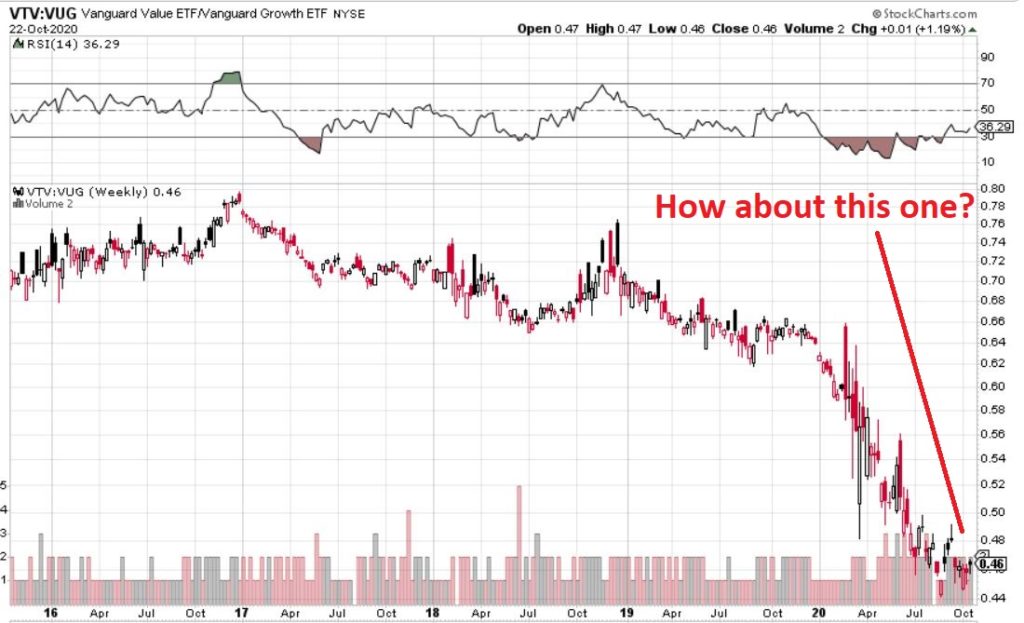
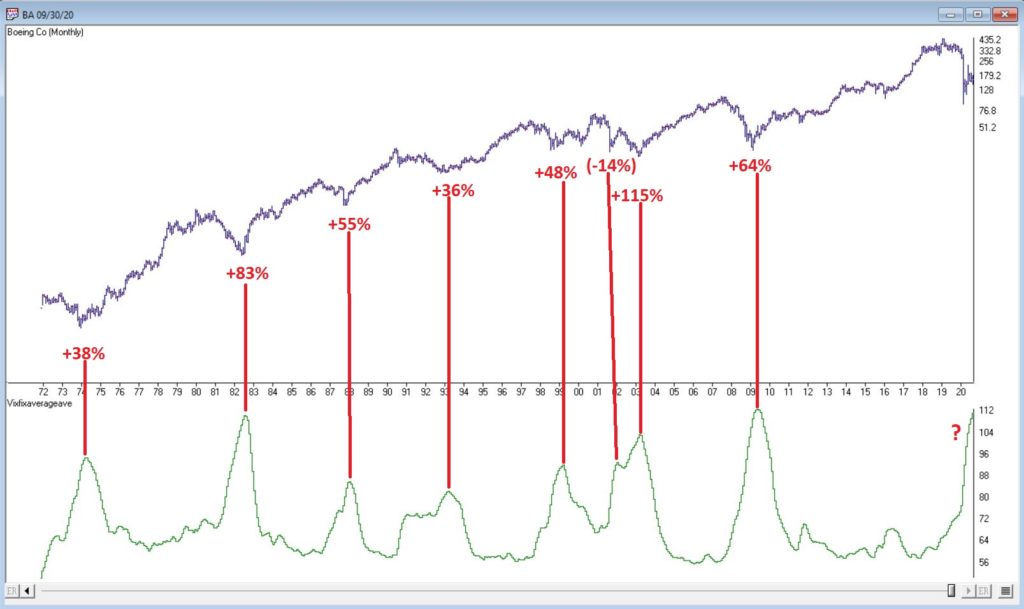
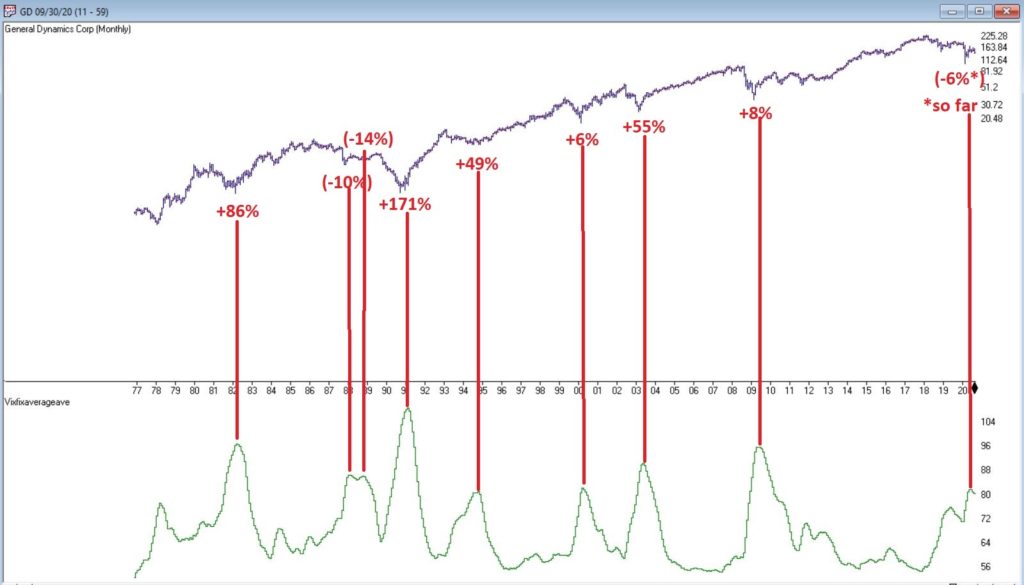
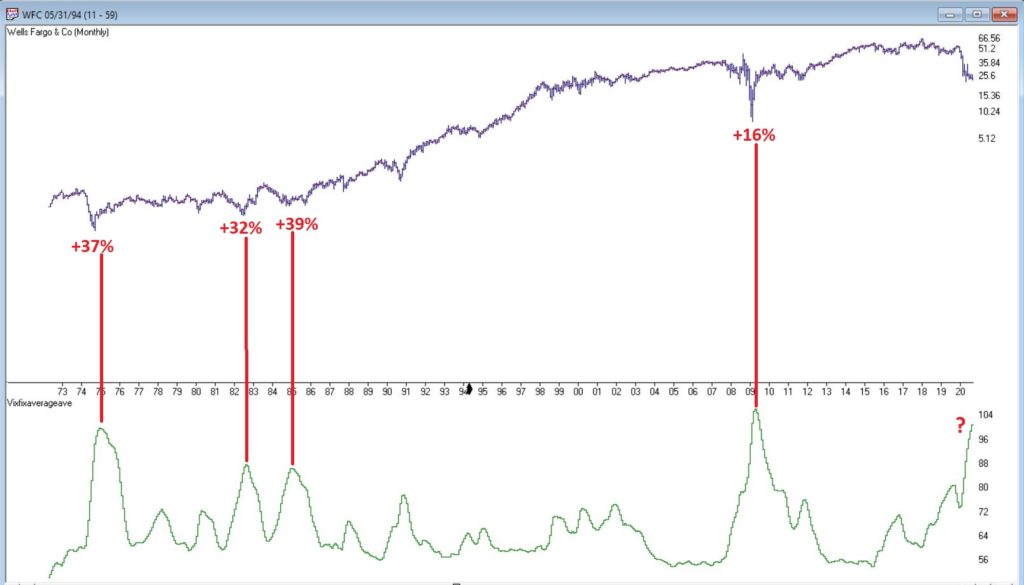
In many ways the markets imitate life. For example, the trend is your friend. You may enjoy your friendship with the trend for an indefinite length of time. But the moment you ignore it – or just simply take it for granted that this friendship is permanent, with no additional effort required on your part – that’s when the trouble starts.
For the stock market right now, the bullish trend is our friend. Figure 1 displays the 4 major indexes all above their respective – and rising – long-term moving averages. This is essentially the definition of a “bull market.”
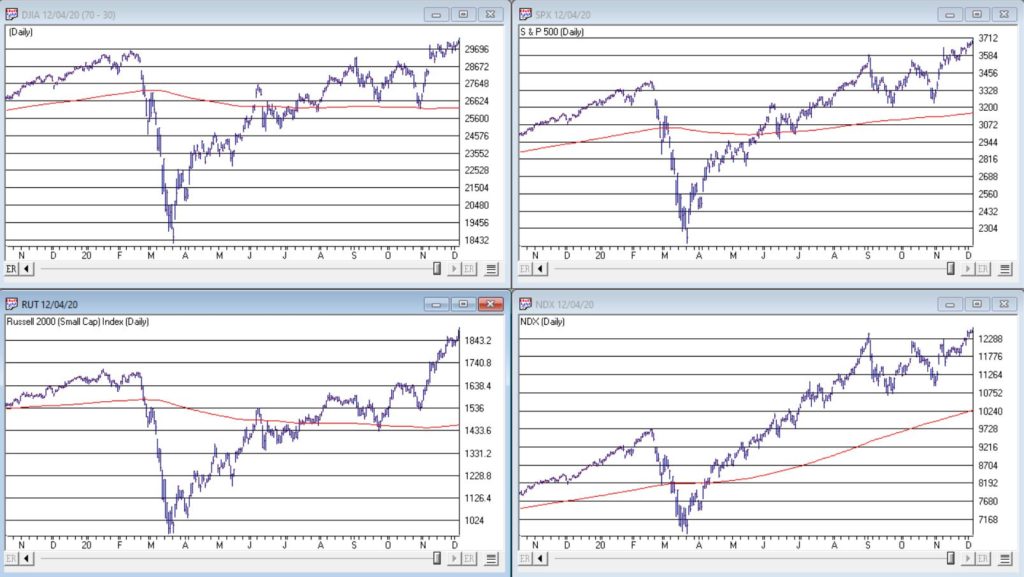
Figure 1 – 4 Major Indexes in Bullish Trends (Courtesy AIQ TradingExpert)
In addition, a number of indicators that I follow have given bullish signals in the last 1 to 8 months. These often remain bullish for up to a year. So, for the record, with my trusted trend-following, oversold/thrust and seasonal indicators mostly all bullish I really have no choice but to be in the bullish camp.
Not that I am complaining mind you. But like everyone else, I try to keep my eyes open for potential signs of trouble. And of course, there are always some. One of the keys to long-term success in the stock market is determining when is the proper time to actually pay attention to the “scary stuff.” Because scary stuff can be way early or in other cases can turn out to be not that scary at all when you look a little closer.
So, let’s take a closer look at some of the scary stuff.
Valuations
Figure 2 displays an aggregate model of four separate measures of valuation. The intent is to gain some perspective as to whether stocks are overvalued, undervalued or somewhere in between.
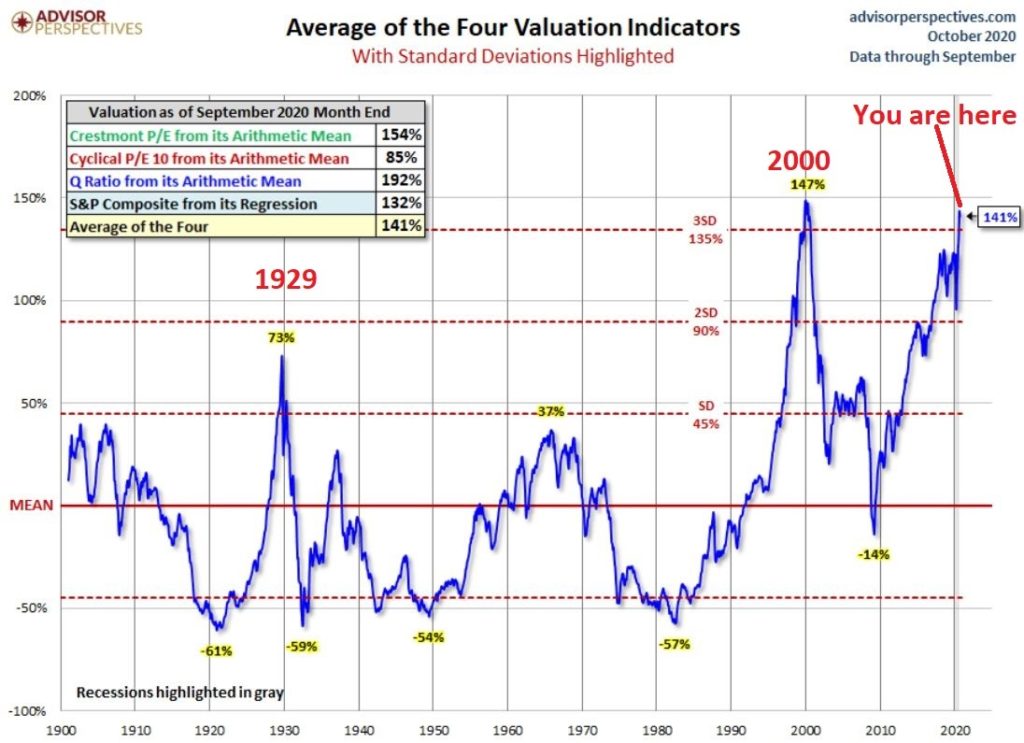
Figure 2 – Stock Market valuation at 2nd highest level ever (Courtesy: www.advisorperspectives.com)
Clearly the stock market is “overvalued” if looked at from a historical perspective. The only two higher readings preceded the tops in 1929 (the Dow subsequently lost -89% of its value during the Great Depression) and 2000 (the Nasdaq 100 subsequently lost -83% of its value).
Does this one matter? Absolutely. But here is what you need to know:
*Valuation IS NOT a timing indicator. Since breaking out to a new high in 1995 the stock market has spent most of the past 25 years in “overvalued” territory. During this time the Dow Industrials have increased 700%. So, the proper response at the first sign of overvaluation should NOT be “SELL.”
*However, ultimately valuation DOES matter.
Which leads directly to:
Jay’s Trading Maxim #44: If you are walking down the street and you trip and fall that’s one thing. If you are climbing a mountain and you trip and fall that is something else. And if you are gazing at the stars and don’t even realize that you are climbing a mountain and trip and fall – the only applicable phrase is “Look Out Below”.
So, the proper response is this: instead of walking along and staring at the stars, keep a close eye on the terrain directly in front of you. And watch out for cliffs.
Top 5 companies as a % of S&P 500 Index
At times through history certain stocks or groups of stocks catch “lightning in a bottle.” And when they do the advances are spectacular, enriching anyone who gets on board – unless they happen to get on board too late. Figure 3 displays the percentage of the S&P 500 Index market capitalization made up by JUST the 5 largest cap companies in the index at any given point in time.
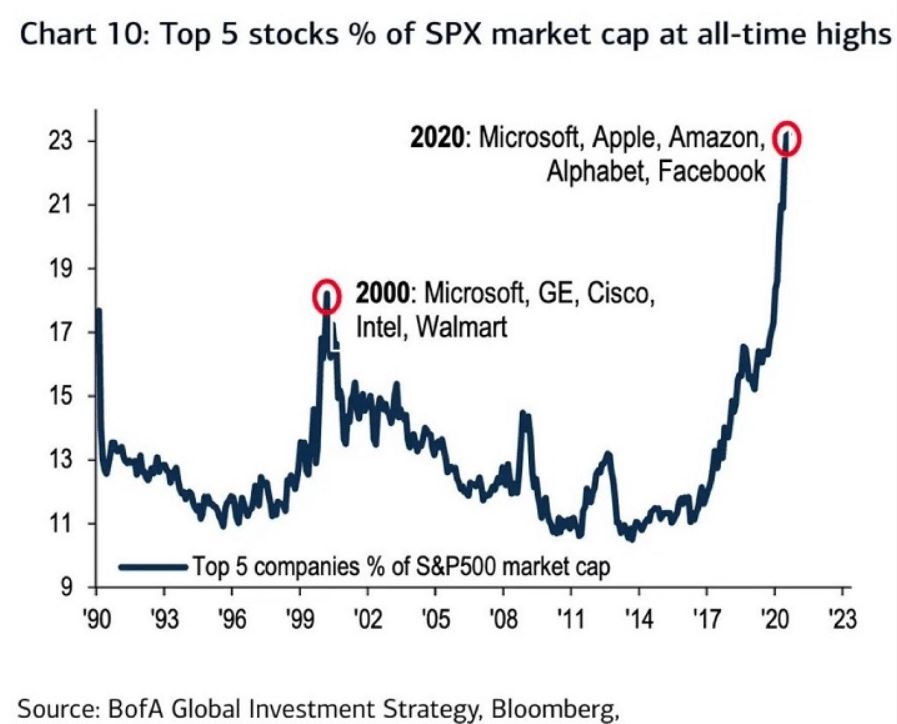
Figure 3 – Top 5 stocks as a % of S&P 500 Index market cap (Courtesy: www.Bloomberg.com)
The anecdotal suggestion is pretty obvious. Following the market peak in 2000, the five stocks listed each took a pretty significant whack as shown in Figure 4.
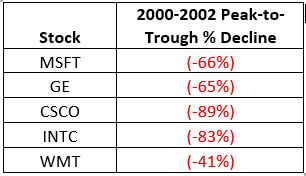
Figure 4 – Top Stocks after the 2000 Peak
Then when we look at how far the line in Figure 3 has soared in 2020 the obvious inference is that the 5 stocks listed for 2020 are due to take a similar hit. And here is where it gets interesting. Are MSFT, AAPL, AMZN, GOOGL and FB due to lose a significant portion of their value in the years directly ahead?
Two thoughts:
*There is no way to know for sure until it happens
*That being said, my own personal option is “yes, of course they are”
But here is where the rubber meets the road: Am I presently playing the bearish side of these stocks? Nope. The trend is still bullish. Conversely, am I keeping a close eye and am I willing to play the bearish side of these stocks? Yup. But not until they – and the overall market – actually starts showing some actual cracks.
One Perspective on AAPL
Apple has been a dominant company for many years, since its inception really. Will it continue to be? I certainly would not bet against the ability of the company to innovate and grow its earnings and sales in the years ahead. Still timing – as they say – is everything. For what it is worth, Figure 5 displays the price-to-book value ratio for AAPL since January 1990.
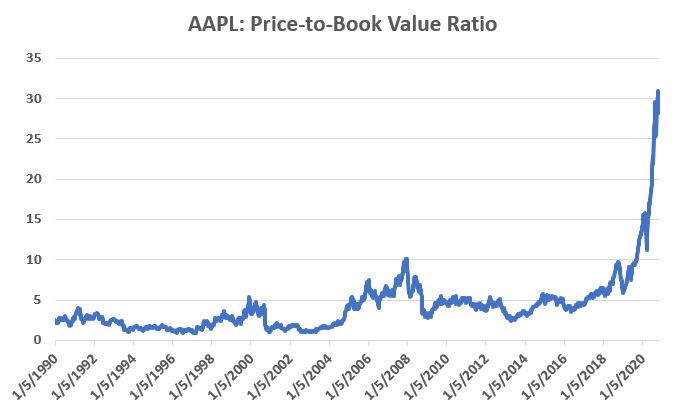
Figure 5 – AAPL price-to-book value ratio (Data courtesy of Sentimentrader.com)
Anything jump out at you?
Now one can argue pretty compellingly that price-to-book value is not the way to value a leading technology company. And I probably agree – to a point. But I can’t help but look at Figure 5 and wonder if that point has possibly been exceeded.
Summary
Nothing in this piece is meant to make you “bearish” or feel compelled to sell stocks. For the record, I am still in the bullish camp. But while this information DOES NOT constitute a “call to action”, IT DOES constitute a “call to pay close attention.”
Bottom line: enjoy the bull market but DO NOT fall in love with it.
Jay Kaeppel
Disclaimer: The information, opinions and ideas expressed herein are for informational and educational purposes only and are based on research conducted and presented solely by the author. The information presented represents the views of the author only and does not constitute a complete description of any investment service. In addition, nothing presented herein should be construed as investment advice, as an advertisement or offering of investment advisory services, or as an offer to sell or a solicitation to buy any security. The data presented herein were obtained from various third-party sources. While the data is believed to be reliable, no representation is made as to, and no responsibility, warranty or liability is accepted for the accuracy or completeness of such information. International investments are subject to additional risks such as currency fluctuations, political instability and the potential for illiquid markets. Past performance is no guarantee of future results. There is risk of loss in all trading. Back tested performance does not represent actual performance and should not be interpreted as an indication of such performance. Also, back tested performance results have certain inherent limitations and differs from actual performance because it is achieved with the benefit of hindsight.