The AIQ code based on Domenico D’Errico’s article in the August issue of Stocks & Commodities magazine, “Portfolio Strategy Based On Accumulation/Distribution,” is shown below.
“Whether you are an individual trader or an asset manager, your main goal in reading a chart is to detect the intentions of major institutions, large operators, well-informed insiders, bankers and so on, so you can follow them. Here, we’ll build an automated stock portfolio strategy based on a cornerstone price analysis theory.”
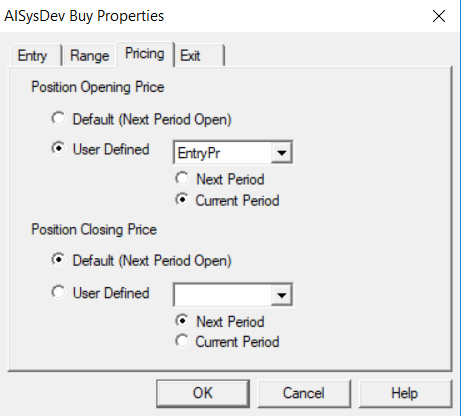
!Portfolio Strategy Based on Accumulation/Distribution !Author: Domenic D'Errico, TASC Aug 2018 !Coded by: Richard Denning 6/10/18 !www.TradersEdgeSystem.com !Portfolio Strategy Based on Accumulation/Distribution !Author: Domenic D'Errico, TASC Aug 2018 !Coded by: Richard Denning 6/10/18 !www.TradersEdgeSystem.com !SET TO WEEKLY MODE IN PROPERTIES !ALSO VIEW CHARTS IN WEEKLY MODE !INPUTS: rLen is 4. consolFac is 75. ! in percent adxTrigger is 30. volRatio is 1. volAvgLen is 4. volDelay is 4. !CODING ABREVIATIONS: H is [high]. L is [low]. C is [close]. C1 is valresult(C,1). H1 is valresult(H,1). L1 is valresult(L,1). !RANGE ACCUMULATION/DISTRIBUTION: theRange is hival([high],rLen) - loval([low],rLen). Consol if theRange < consolFac/100 * valresult(theRange,rLen). rRatio is theRange/valresult(theRange,4)*100. !AVERAGE TRUE RANGE ACCUMULATION/DISTRIBUTION: avgLen is rLen * 2 - 1. TR is Max(H-L,max(abs(C1-L),abs(C1-H))). ATR is expAvg(TR,avgLen). ConsolATR if ATR < consolFac/100 * valresult(ATR,rLen). atrRatio is ATR / valresult(ATR,4)*100. !ADX ACCUMULATION/DISTRIBUTION: !ADX INDICATOR as defined by Wells Wilder rhigh is (H-H1). rlow is (L1-L). DMplus is iff(rhigh > 0 and rhigh > rlow, rhigh, 0). DMminus is iff(rlow > 0 and rlow >= rhigh, rlow, 0). AvgPlusDM is expAvg(DMplus,avgLen). AvgMinusDM is expavg(DMminus,avgLen). PlusDMI is (AvgPlusDM/ATR)*100. MinusDMI is AvgMinusDM/ATR*100. DIdiff is PlusDMI-MinusDMI. Zero if PlusDMI = 0 and MinusDMI =0. DIsum is PlusDMI+MinusDMI. DX is iff(ZERO,100,abs(DIdiff)/DIsum*100). ADX is ExpAvg(DX,avgLen). ConsolADX if ADX < adxTrigger. !CODE FOR ACCUMULATIOIN/DISTRIBUTION RANGE BREAKOUT: consolOS is scanany(Consol,250) then offsettodate(month(),day(),year()). Top is highresult([high],rLen,^consolOS). Top0 is valresult(Top,^consolOS) then resetdate(). Bot is loval([low],rLen,^consolOS). AvgVol is simpleavg([volume],volAvgLen). Bot12 is valresult(Bot,12). BuyRngBO if [close] > Top and ^consolOS <= 5 and ^consolOS >= 1 and Bot > Bot12 and valresult(AvgVol,volDelay)>volRatio*valresult(AvgVol,volAvgLen+volDelay). EntryPrice is [close]. Sell if [close] < loval([low],rLen,1). ExitPrice is [close].
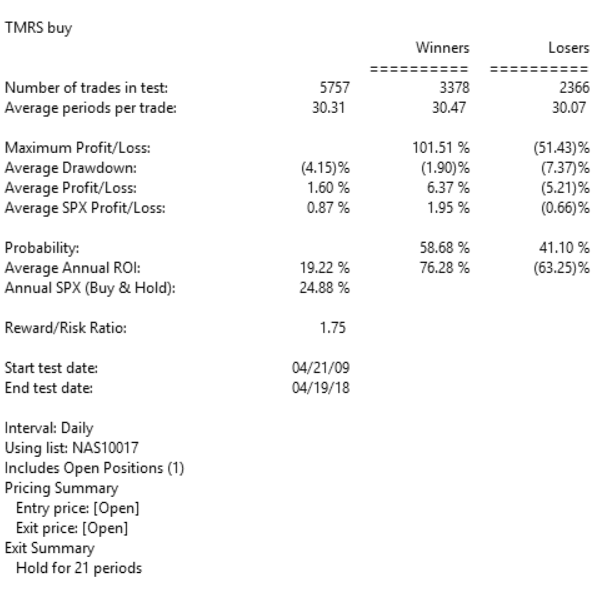
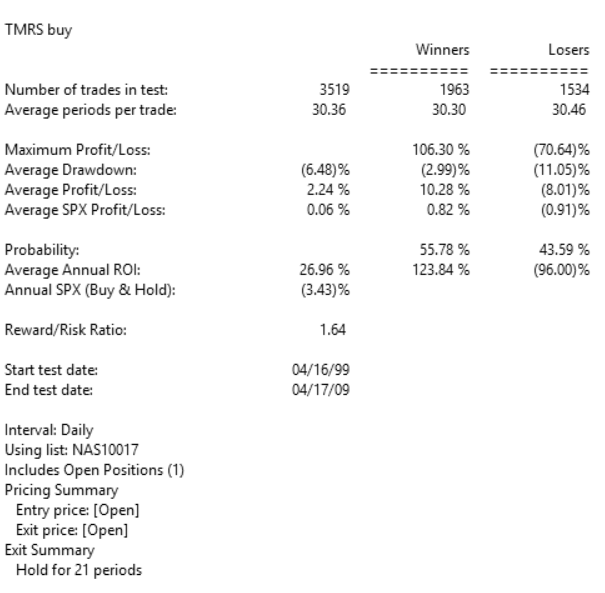
Figure 9 shows the summary backtest results of the range accumulation breakout system using NASDAQ 100 stocks from December 2006 to June 2018. The exits differ from the author’s as follows: I used two of the built-in exits — a 20% stop-loss and a profit-protect of 40% of profits once profit reaches 10%.

FIGURE 9: AIQ. Here are the summary results of a backtest using NASDAQ 100 stocks.
Figure 10 shows a color study on REGN. The yellow bars show where the range accumulation/distribution shows a consolidation.

FIGURE 10: AIQ. This color study shows range consolidation (yellow bars).